Deimos (chaand)
Appearance
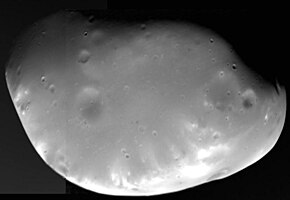 Deimos ke chhaapa | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Asaph Hall |
| Discovery date | 12 August 1877 |
| Designations | |
Designation | Mars II |
| Pronunciation | /ˈdaɪməs/[1] to /ˈdiːməs/[2] or as Greek Δεῖμος (approximated /ˈdeɪmɒs/)[3] |
Named after | Δεῖμος |
| Adjectives | Deimian /ˈdaɪmiən/[4] |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| Epoch 23 September 2012 (JD 2456191.5) | |
| Periapsis | 23455.5 km |
| Apoapsis | 23470.9 km |
| 23463.2 km[5] (6.92 Mars radii) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.00033[5] |
| 1.263 d[5] (30.312 h) | |
Average orbital speed | 1.3513 km/s[6] |
| Inclination | 0.93° (to Mars's equator) 1.791° (to the local Laplace plane)[5] 27.58° (to the ecliptic) |
| Satellite of | Mangalgrah |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 16.08 × 11.78 × 10.22 km (0.16 × 0.12 × 0.10 km)[7] |
Mean radius | 6.27±0.07 km[7] |
| 522±8 km2[7] | |
| Volume | 1033±19 km3[7] |
| Mass | 1.4762×1015 kg[6] |
Mean density | 1.465±0.051 g/cm3[7] |
| 0.003 m/s2[6] (306 µg) | |
| 5.556 m/s (20 km/h)[6] | |
| Synchronous[5] | |
| Albedo | 0.068±0.007[8] |
| Temperature | ≈ 233 K |
| 12.89[9] | |
mos (chaand), nai to Mars II, Mangalgrah (Mars) ke chhotkana chandarma hae. Duusra chandarma ke naam Phobos hae. Iske naam Greek me se aais hae aur iske matlab "terror" hae. Ii har 30.3 ghantaa me Mars ke parikramaa kare hae. Deimos ke diameter khaali 15 kilomters hae aur ii craters se bharaaa hae. Iske 12 August 1877 me Asaph Hall paais rahaa.
Saur mandal (Solar System)
| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suraj • Heliosphere |
Grah (Planets) ☾ = Chaand ∅ = rings |
Budhgrah (Mercury) | Sukhgrah (Venus) | Dunia (Earth) ☾ | Mangalgrah (Mars) ☾ | ||
| Brahaspati (Jupiter) ☾ ∅ | Sanigrah (Saturn) ☾ ∅ | Arungrah (Uranus) ☾ ∅ | Varungrah (Neptune) ☾ ∅ | ||||
| Bauna grah (Dwarf planet) |
Ceres | Pluto ☾ | Haumea ☾ | Makemake | |||
| Eris ☾ | |||||||
| Small Solar System bodies |
Chhota tara (Asteroid) (minor planets) |
Groups and families: Vulcanoids · Near-Earth asteroids · Asteroid belt Jupiter Trojans · Centaurs · Neptune Trojans · Asteroid moons · Meteoroids · Pallas · Juno · Vesta · Hygiea · | |||||
| See also the list of asteroids. | |||||||
| Trans- Neptunians |
Kuiper belt – Plutinos: Orcus · Ixion – Cubewanos: Varuna · Quaoar · Huya | ||||||
| Scattered disc: Sedna | |||||||
| Jhaarru | Lists of periodic and non-periodic comets Damocloids · Hills cloud · Oort cloud | ||||||
| See also the list of solar system objects | |||||||
| Ii vigyan article ek chhota panna hae. Aap iske lamba karke Wikipedia ke madat kare saktaa hae. |
- ↑ The Century Dictionary and Cyclopedia (1914)
- ↑ "Moons of Mars – the Center for Planetary Science". Archived from the original on 2023-04-09. Retrieved 2024-02-28.
- ↑ "Deimos". Lexico UK English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. Archived from the original on 22 March 2020.
- ↑ Harry Shipman (2013) Humans in Space: 21st Century Frontiers, p. 317
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 "HORIZONS Web-Interface". NASA. 21 September 2013. Retrieved 4 December 2013.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedNASA - ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedErnst2023 - ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedJPLSSD - ↑ "Mars' Moons".

