Turkish bhasa
| Turkish | |
|---|---|
| Türkçe | |
| Pronunciation | [ˈt̪yɾkˌtʃe] |
| Spoken in | Albania, Azerbaijan[1], Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Greece, Hungary, Iraq, Kosovo, Lebanon, Republic of Macedonia, Moldova, Montenegro, Northern Cyprus, Palestine, Romania, Russia, Serbia, Syria,[2] Turkey, Uzbekistan, and by immigrant communities in Austria, Belgium, France, Germany, Italy, The Netherlands, Switzerland, United Kingdom, United States, and other countries of the Turkish diaspora |
| Region | Anatolia, Cyprus, Balkans, Caucasus, Central Europe, Western Europe |
| Native speakers | over 63 million worldwide (date missing) |
| Language family | |
| Writing system | Latin alphabet (Turkish variant) |
| Official status | |
| Official language in | *See Cyprus Dispute. **In municipalities with more than 20% Turkish speakers. ***Turkish is one of regional languages. |
| Regulated by | Turkish Language Association |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | tr |
| ISO 639-2 | tur |
| ISO 639-3 | tur |
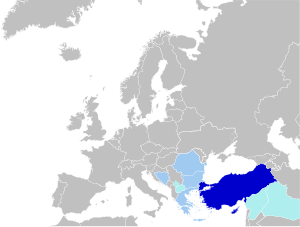 | |
Turkish (Türkçe) ek bhasa hae jisme Republic of Turkey, Cyprus, Bulgaria, Greece, aur pahile ke Ottoman Empire ke des, ke log baat kare hae. Europe me bhi kuchh million emigrants hae jon ki turkish me baat kare hae.
Turkish, Altaic language family ke ek Turkic bhasa hae. Turkish me vowel harmony hae, jaise ki Finnish aurHungarian me rahe hae. Turkish me word order hae: Subject Object Verb (SOV).
Turkish ke, 1000 AD se 1928 tak, Arabic Alphabet me lkha jawat rahaa . Ottoman Empire me, Turkish language ke ek rich literature rahaa, aur isme dher book likha gais rahaa. Lekin, Mustafa Kemal Atatürk iske badal ke Latin Alphabet kar diis kahe ki uu mangat rahaa ki uske des western des ke rakam hoe ke huan ke technologic improvements se faaeds uthaae. Iske kaaran dher Turkish log ii change se pahile likha ais book ke nai parrhe sake hae.
Ii bhasa duusra Turkic languages, jisme Uzbek, Turkmen, aur Kazakh hae, se ralated hae. Kuchh ii biswas kare hae ki Turkish Altaic family of languages ke hae, jisme Japanese, Mongolian, aur Korean hae.
Turkish bhasa me ginti
[badlo | source ke badlo]| Number Turkish me | Number Fiji Hindi me |
|---|---|
| bir | ek |
| iki | dui |
| üç (üch) | tiin |
| dört | chaar |
| beş (besh) | paanch |
| altı | chhe |
| yedi | saat |
| sekiz | aath |
| dokuz | nau |
| on | das |
Hafta ke din
[badlo | source ke badlo]| Fiji Hindi | Turkish |
|---|---|
| Sombaar | pazartesi |
| Mangar | salı |
| Budh | çarşamba (char-shamba) |
| Bif | perşembe (pershembe/urdu: panj-shamba) |
| Suk | cuma (jumaa) |
| Sanichar | cumartesi (jumartesi) |
| Etwaar | pazar |
References
[badlo | source ke badlo]- ↑ Taylor & Francis Group (2003) (in English). Eastern Europe, Russia and Central Asia 2004. Routledge. pp. p. 114. ISBN 978-1857431872. http://books.google.com/books?id=NI1G_9j1AhcC&pg=PT134&dq=1999+census+azerbaijan+turkish&lr=&hl=en&sig=lhkBOxL4bArgFBJRuOgLYxVfRUA. Retrieved 2008-03-26.
- ↑ name="Turkish Weekly Aksiyon">"Syrian Turks". Archived from the original on 2009-04-20. Retrieved 2009-01-19.
- ↑ "Introductory Survey". Archived from the original on 2008-06-22. Retrieved 2009-01-19.
- ↑ Numbers in Million-Speaker Languages
- ↑ Days of the week in Turkish
